Understanding the Difference Between Data Analytics and Business Intelligence

- Source: AndreyPopov from Getty Images
Every business, from a small café to a multinational corporation, relies on data to make decisions. Whether tracking daily sales, understanding customer preferences, or predicting market trends, data is the key to staying ahead. While businesses collect massive amounts of data, the ways they process and interpret that data can differ significantly. Some companies depend on Business Intelligence (BI) tools to analyze past performance, while others utilize Data Analytics to forecast future trends and identify deeper patterns. Though they may seem similar, Data analytics vs business intelligence affects how businesses strategize and grow.
To illustrate, imagine a business as a ship. Business Intelligence serves as a compass and a map, indicating where the ship has been and providing clear direction based on past journeys. Data Analytics, in contrast, involves reading the weather and ocean currents, predicting what lies ahead, and adjusting the route accordingly. Both are essential, but they fulfill different purposes.
This article will help you understand more about Data analytics vs business intelligence and why they are foundational for organizations. Before discussing the difference between data analytics and business intelligence, we need to get clear on what each one means.
What Is Business Intelligence?

Consider a supermarket chain monitoring daily sales. BI tools collect and present data in dashboards, displaying which products are selling best, how different store locations are performing, and which hours generate the most traffic. These insights help business leaders track key performance indicators (KPIs) and make necessary adjustments.
BI systems work with structured data, meaning the information comes from predefined sources like databases and data warehouses. Unlike data analytics, which requires advanced modeling and statistical analysis, BI tools are designed to be user-friendly, making it easier for executives and managers to interpret data quickly.
What Is Data Analytics?
Data Analytics is the process of examining raw data to discover trends, patterns, and correlations that help businesses make accurate decisions. It doesn’t just summarize past performance; it provides info on why things happened and what could happen next. Companies can forecast trends, identify risks, and make operations smooth by applying statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and predictive techniques.
For example, take an online retailer like Amazon. Instead of just tracking how many sales occurred last month, data analytics helps them predict which products will be in demand next season. By analyzing customer behavior, purchasing patterns, and even external factors like economic trends, businesses can make strategic decisions before trends fully emerge. Industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, and technology rely heavily on data analytics.
Data analytics is divided into four key types:
- Descriptive Analytics (What happened?) – Summarizing past events.
- Diagnostic Analytics (Why did it happen?) – Identifying reasons behind patterns.
- Predictive Analytics (What will happen next?) – Using data models to forecast future trends.
- Prescriptive Analytics (What should we do about it?) – Recommending actions based on data-driven insights.
Purpose of Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Data analytics vs business intelligence becomes clearer when understanding their purpose. Business Intelligence focuses on tracking and reporting, while data analytics concentrates on deeper exploration and predictions. BI is essential for companies that need structured data visualization to monitor past performance and make operational adjustments. Data analytics is more strategic, it’s about discovering patterns, understanding relationships, and making future-oriented decisions. For instance, a clothing retailer might use BI to generate reports on last quarter’s best-selling items. To understand why those items performed well and predict the next big trend, they would turn to data analytics.
The Difference Between Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
This table simplifies the Data analytics vs business intelligence, showing how both help businesses but serve different purposes.
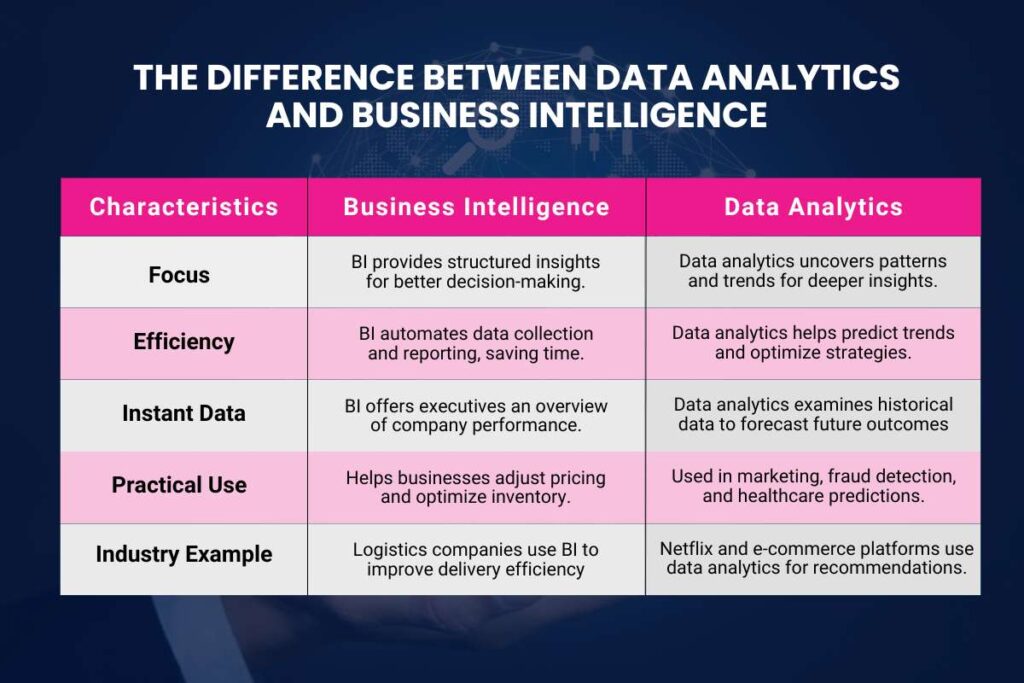
| Characteristics | Business Intelligence | Data Analytics |
| Focus | BI provides structured insights for better decision-making. | Data analytics uncovers patterns and trends for deeper insights. |
| Efficiency | BI automates data collection and reporting, saving time. | Data analytics helps predict trends and optimize strategies. |
| Instant Data | BI offers executives an overview of company performance. | Data analytics examines historical data to forecast future outcomes. |
| Practical Use | Helps businesses adjust pricing and optimize inventory. | Used in marketing, fraud detection, and healthcare predictions. |
| Industry Example | Logistics companies use BI to improve delivery efficiency. | Netflix and e-commerce platforms use data analytics for recommendations. |
Advantages of Business Intelligence
BI provides businesses with structured, easy-to-access insights that improve decision-making. It’s particularly valuable for executives who need an overview of the company’s performance without complex analysis. One of its biggest advantages is efficiency. BI automates data collection and reporting, reducing the time employees spend manually compiling reports. This means companies can respond quickly to changes in the market, adjust pricing strategies, and optimize inventory management. Additionally, BI helps organizations identify inefficiencies. A logistics company, for example, might notice through BI reports that certain delivery routes take longer than expected. By addressing these inefficiencies, they can save costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Advantages of Data Analytics
While BI focuses on making data accessible, data analytics unlocks deeper insights. By analyzing historical data, businesses can predict future trends, personalize marketing strategies, and uncover hidden opportunities. A streaming service like Netflix doesn’t just track which shows are most popular, it uses data analytics to recommend content based on a viewer’s watch history. Similarly, e-commerce platforms analyze browsing and purchase patterns to deliver personalized product recommendations. Another major advantage is risk assessment. Financial institutions rely on predictive analytics to detect suspicious transactions and prevent fraud. In healthcare, data analytics helps doctors predict disease outbreaks and optimize patient treatment plans.
Data Analytics vs Business Intelligence: How They Work Together?
Industry Examples
- Retail Industry: Business Intelligence tracks sales numbers, while Data Analytics predicts which products will trend in the next quarter.
- Healthcare: BI monitors hospital readmission rates, while analytics predicts which patients are at risk.
- Finance: BI helps banks manage financial statements, while analytics detects fraud patterns in transactions.
- Marketing: BI reports campaign success, while analytics predicts customer buying behavior for future strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between data analytics vs business intelligence is crucial for businesses looking to maximize their data’s potential. BI helps companies track and measure performance, ensuring smooth operations. Data Analytics goes deeper, identifying patterns, predicting trends, and driving growth. Businesses that integrate BI for reporting and data analytics for insights allow them to understand where they stand and prepare for the future. Both of these are helpful for businesses to sustain in the current competitive market.